Rectification Of Errors in Accounting

Unintentional mistakes or accounting ignorance done at the time of recording or processing which results in some difference in financial statements with that of actual figures of the financial statement are known as errors of accounting. These errors are considered non- fraudulent as they are done unintentionally and not with a view to deceive someone or not with a view to withhold the information from the users of financial statements.
If some errors are identified, it is required to restate the financial statements. If these errors are significantly affecting the previous reports, usually it is required to restate the original financial statements.
If the total of credit balance of all accounts and debit balances of all account does not match, it means that some errors have been committed and those errors could have occurred at any stage of accounting process. Every debit of a transaction will be always followed by corresponding credit and vice versa. The tallying of the two totals of trial balance ensures the arithmetical accuracy but never give assurance on accounting accuracy.
TYPES OF ACCOUNTING ERRORS
Accounting errors can be broadly classified into two namely

Errors of principle
Generally accepted accounting policies are the governing principles of transactions while getting recorded in accounting process. Any ignorance or violation of such results will end up in errors affecting accounting process. Such errors are called errors of principles. Recording an asset purchased in a purchase register is a kind of violating principle. Trial balance will never disclose errors of principles.
Clerical errors
These are the errors committed by the accountant or any other accounting professional in the normal course of accounting process. Clerical errors can be because of many manual deeds while posting, journalizing, etc
Different types of clerical errors are namely
1. Errors of omission
- Errors of complete omission
- Errors of partial omission
2. Errors of commission
- Errors of recording
- Errors of posting
- Errors of casting
- Errors of carrying forward.
3. Compensating errors
Errors of omission
The complete or partial omission of a transaction will be resulting in errors. Such omission may or may not tally the trial balance. Errors of omission are again classified into two:
- Errors of complete omission - This occurs when an entry or transaction is completely or fully ignored from getting recorded. Total ignorance of a transaction will not affect the trial balance but will give wrong information via financial statements. For example, a credit sale of a total amount of 1, 00, 000 which is not at all recorded in the books of accounts. This omission will affect sales turnover and debtor balance. But as the transaction’s debit and credit is ignored together it will not affect trial balance.
- Errors of partial omission - When in the accounting process cycle, recording of any one aspect of transaction is ignored, it can be either debit part or the credit part of the transaction. This will affect the trial balance; it will not be tallied at all. Example - a credit sale of 1, 00, 000 transaction is entered in sales book which the credit aspect is recorded but the corresponding debtor is not recorded. That will result in the debit total to be 1, 00, 000 less than the credit total.
Errors of commission
Errors of commission mostly affect the trial balance. It can be an error which arises at the time of posting, casting, totaling and carrying forward. These errors are further subdivided into
- Errors of recording – This is an error which happens at the basis recording level of accounting process; that is journalizing the entry. This mostly does not affect the trial balance.
- Errors of posting – These are errors which arise when information are wrongly carried or entered in ledger. This happens when right amount is taken to wrong side of the correct account, right amount to right side of wrong account, wrong amount in the right side of the right account, etc.
- Errors of casting – These errors are also considered as errors of totaling. This occurs when a mistake is committed while totaling the subsidiary books. If the wrongly totaled amount is more than the actual, then it is called overstated and if it is less it is called an understatement.
- Errors of carrying forward – When at the time of carrying forward of balance from one page to another page of the same account or when the closing balance of a period is mismatching with the opening balance of the same account then an error of carrying forward occurs. This will always affect the trial balance.
Compensating errors
Compensating errors are those errors which are adjusted by some other error which neutralize each other. Such errors never affect the trial balance. This error occurs when overstated or understated credit of some account is tallied with an overstated or understated debit of some other account. Example - If a total of a purchase of asset and normal operating sales both are overstated, it will compensate each other.
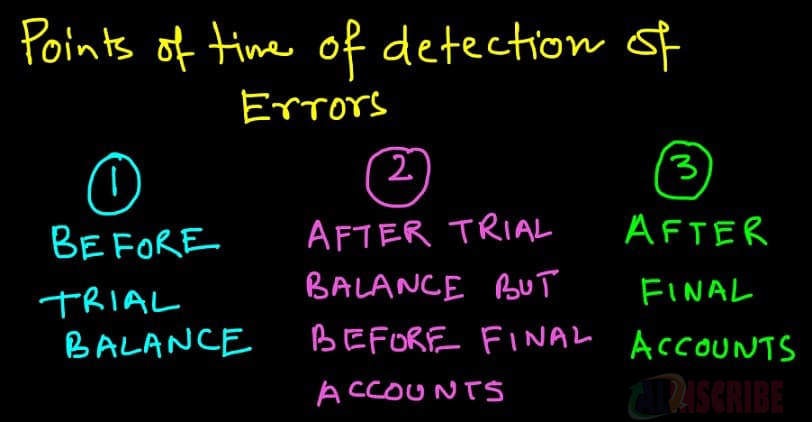
Errors could be found or detected at any point of time or at any stage and the rectification procedure will be based on it.
Rectification of Errors
To rectify an error, the following step by step process has to be initiated
- "What is the error" – We should first find out what the error is by ascertaining what was actually done.
- "Finding the correct record"- Next step is to identify the right entry.
- "Rectify it" – Rectification is done by considering what ought to have been done and what has been done.
The following illustrations will help in better understanding the concept rectification of errors,

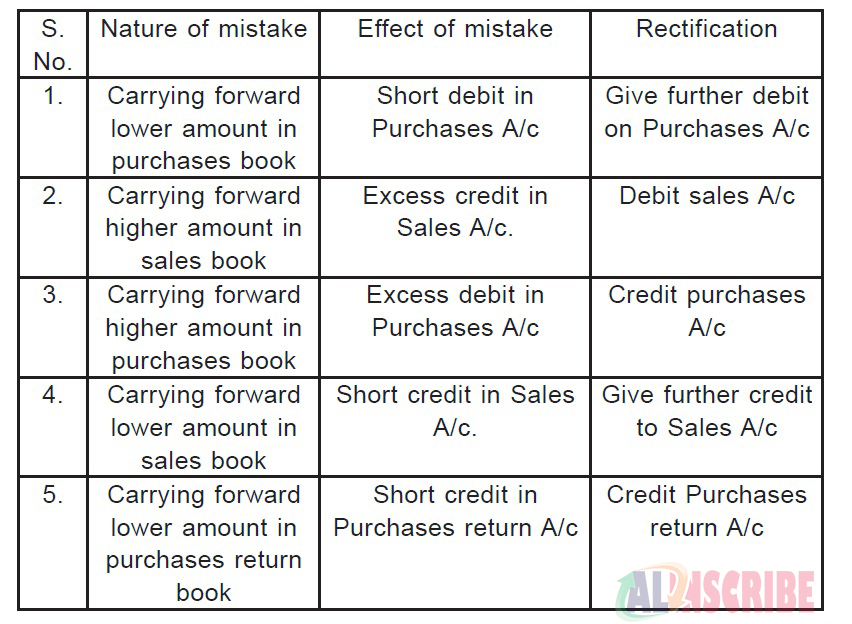

Illustration 2:


Suspense account
When it is difficult to find the difference or mistakes before heading to financial statements preparation, the difference can be transferred to an imaginary or newly opened temporary account named as suspense account. If debit balance is more in trial balance then the difference is credited in suspense account and vice versa.
|
Stage |
|
How rectified |
|
Rectify before preparing of trial balance |
Errors are rectified before getting it transferred to suspense account |
By debiting or crediting the corresponding account with giving enough explanatory note in respective columns |
|
Rectify after preparation of trial balance |
Errors are rectified after transferring difference to suspense account. |
By passing a journal entry with the respective accounts or accounts affected by the error and suspense account. |
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.