Trial Balance - Definition, examples and explanation

Trial balance is basically prepared at the end of an accounting period, which acts as the first step towards the preparation of financial statements. Trial balance is a list of closing balances of all the ledger accounts at a specific time that is on a particular date and in trial balance, all the ledger balances are sorted and segregated as debit balance and credit balance. In other words, Trial balance is just a consolidated statement showing the balances of accounts that are to be transferred to Balance sheet.
If all the accounting transactions are properly recorded, journalized and posted, the totaling is also automatically done without any mistake. Then, the total balance of credit will be equal to that of debit. All the ledgers can be classified into Assets, Liabilities, Income, Expenses, and Capital generally. Capital can be also called as Owner’s fund. In all these accounts, expenses and assets normally have debit balances. And in case of incomes, capital and liabilities, it will have credit balances. Generally, trial balance acts as working papers, but they are documents which give a basis to the accountants for the purpose of preparing financial statements.
Trial balance helps out to verify whether our journalizing, posting and totaling work are being done in the process of accounting. If the total balance of debit is equal to that of sum total of credit, it points out that all the processes in the accounting and is trustworthy and is without any bias or errors (except to some errors which are discussed in subsequent articles) to an extent.
Trial balance ensures that for all the transactions both debit and credit entry made for the corresponding entry at the same time. Trial balance also to an extent assures arithmetical accuracy of accounting entries.
If the totals of both the sides in trial balance do not match with each other or doesn’t agree, the difference is to be enquired and cleared off before stepping forward for the preparation of financial statements. Trial balance supports to find errors and clarify those errors.
Trial balance also has some limitations. Trial balances will fail to identify compensating errors, full omission, and errors of principal. A trial balance cannot be considered as evidence because of these limitations.

Description of a Trial Balance
- Title provided at the top mentions the name of the entity and the accounting period for which trial balance is prepared
- In account title column, ledger account name is listed out.
- Each account balances are extracted from the ledgers and are presented in trial balance in amount columns. Asset and Expenses will be having debit balances which will be entered in left side amount column which is the debit column and Income, Liabilities and Equity accounts will be having credit balances which is to be presented in the right-hand amount column otherwise known as credit column.
- After totaling both columns, subtotal has to be given at the bottom of the respective columns.
Steps to be followed while preparing trial balance
- Ledger accounts have to be closed and balances should be found at the end of the accounting period.
- Ledger account balances are to be taken to the trial balance
- If in the trial balance the total agrees with each other, it means that there is no issue. If the sum is not agreeing with each other, trial balance is cast and errors are to be identified.
- In such cases, we should create a new account called suspense account (it is an adjusting account which is created basically for a temporary purpose) which is meant to agree with the trial balance totals until corrections are accounted for.
- If errors are found, corrective entries have to be passed and posted.
EXAMPLE
TRIAL BALANCE OF X LTD FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 / 03 / 2017
|
SL NO |
ACCOUNT TITLE |
DEBIT AMOUNT |
CREDIT AMOUNT |
|
1 |
BANK |
1, 00, 000 |
|
|
2 |
10, 000 |
|
|
|
3 |
ACCOUNTS RECIEVABLE |
20, 000 |
|
|
4 |
5, 000 |
|
|
|
5 |
PREPAID EXPENSES |
7, 000 |
|
|
6 |
FURNITURE |
10, 000 |
|
|
7 |
FIXED ASSETS |
30, 000 |
|
|
8 |
LOAN FROM BANK |
|
50, 000 |
|
9 |
OTHER LOANS |
|
40, 000 |
|
10 |
TRADE PAYABLES |
|
12, 000 |
|
11 |
OTHER CREDITORS |
|
10, 000 |
|
12 |
CAPITAL |
|
55, 000 |
|
13 |
WAGES PAYABLES |
|
10, 000 |
|
14 |
PREAPAID INCOMES |
|
5, 000 |
|
|
TOTALS |
1, 82, 000 |
1, 82, 000 |
This is an example is just to give an idea of how trial balance is prepared and how each items are drafted.
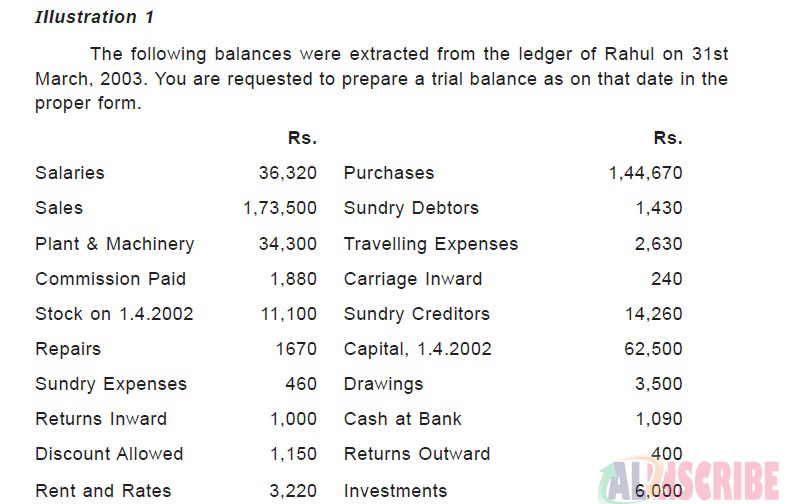
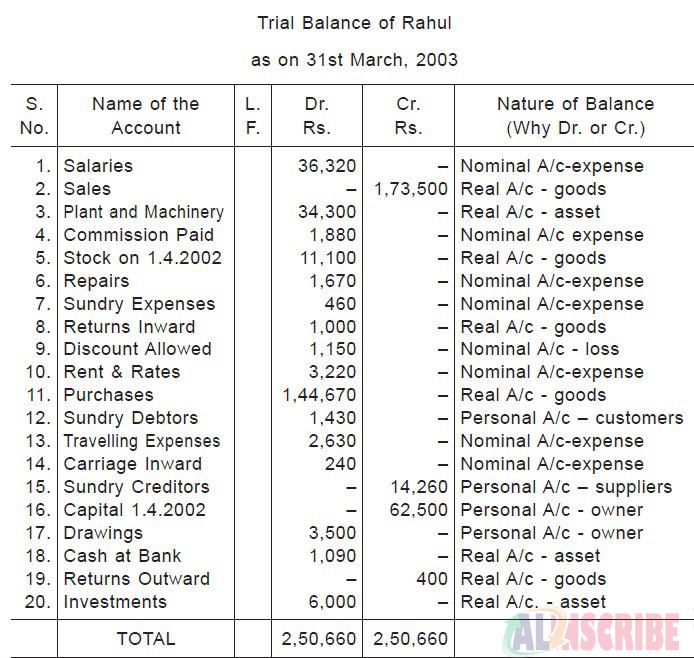
The following example will clearly make understand the trial balance in a easy way
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.