A Detailed Discussion on Books Of Accounts

Books of accounts are the records which are prepared and maintained of the day to day activity of business. Books of accounts are of mainly of two types, namely manual books of accounts and computerized books of accounts.
Manual books of accounts are the manually maintained traditional journal, ledger and columnar books which are used to record each transaction. These records are of less cost, hand written mostly maintained by small firms.
Computerized book keeping is the result of growing technology which gives out the efficient, fast and mostly error free process of recording transactions. It is comparatively costlier and used by medium and large enterprises.

BOOKS OF ACCOUNTS IN GENERAL
- General Journal
- Ledger
- Sales Book and Sales Returns book
- Cash Book
- Purchases Book and Purchase Returns book
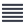
General Journal
The process of recording transaction in a journal is called journalizing. Journal is also called by the name subsidiary book. With the help of golden rules of accounting and other concept we have to identify which account is to be credited and which account is to be debited.
Identification of debit and credit and recording it as an accounting entry is called journalizing. Journal is the first book in which accounting entries are made. Most of the time invoices, bills and other documents act as the source of entry and act as a proof or evidence. All the transactions in journal are entered in chronological order for the ease of verification and reliability.
Each journal entry in a journal will have two accounts one debited and another account which is credited. It will be also including date, debit amount and credit amount details. Each journal entry will be followed by a brief description of the entry as a phrase always starting with the word being. The different columns of journal are namely date particulars, ledger folio, debit amount and credit amount. Ledger folio is the column which acts as a link between the accounts (corresponding the entry) with that of journal.
Journal entries can be single or compounded entry. Single entry means there will be only one debit and one credit, but if it is a compounded entry there can be two are more debits or credits or both in the same entry. Compounded entries are sometimes formed by clubbing two or more single entries.
And while preparing journal if it’s more than one page it is must to total both debit amount column and credit amount column of each page and carry forward to next page also. Always the total of debit amount column and credit amount column should be equal.
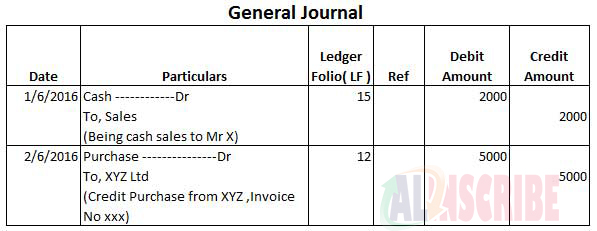
Suppose here are some transactions-
- Cash sales to Mr. X of 100
- Purchased fixed assets worth 1000
- Paid salary of 100 and office expenses of 10
- Purchased goods worth 100 and received a cash discount of 15
LEDGER
When journal entries are recorded of about one transaction in journal, different accounts are sorted, classified and listed into its respective and corresponding account and books as the case may be. The book which holds all these ledgers (real, personal and nominal) is called ledger book. Ledger book is the principal book of accounts.
To discuss about structure of ledger account, it mainly has two sides-debit (left part of the account) and credit (right part of the account).
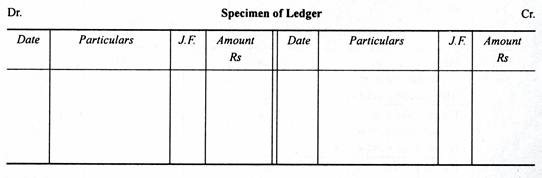
Each separate side of the debit and credit side has four columns.
- Date
- Particulars
- Journal folio i.e.(representing the page from where the journal entries are taken for posting) and
- Amount.
It is a must to total both the amount columns of accounts. The amount of difference arising thereof is the balance of accounts which is to be carried forwarded. While opening an account in the new accounting period or page we have to take brought forward balance which is the carried forward amount.
Dr. Cr.
|
Date |
Particulars |
JF |
Amount |
Date |
Particulars |
JF |
Amount |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The words ‘To’ and ‘by’ are used while posting journal entries into ledger. By’ is used with the accounts written in the particular column of the credit side, meanwhile ‘To’ is used in the particular column of debit side.
Sales Book:
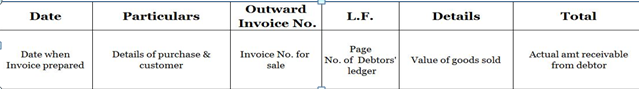
Sales book is maintained by the entity to record all the transactions of credit sales done by it. This means that, cash sales are not recorded in the sales book but are directly recorded in the cash book as cash is received and is flowed into the business at the time of sale. The Credit sales are recorded in a separate book as the sale is done on a particular date and the consideration is paid to the entity by cheque or settled at a later date. Since the money is realized on a later date, the company has to have a match between the sales made on credit, the amount realized on account of each invoice and also the list of parties paid. This is the reason the buyers who buy on credit will have a separate ledger account in the books of the company and the respective reference page number is mentioned against each sale transaction in L.F. column. The sales day book is totalled on a daily basis and then transferred to the main sales ledger and the total of sales ledger is transferred to Income statement at the end of the year. This sales day book is ordinarily used only in the case of manual accounting systems and not in the computerized accounting systems.
Format of sales day book is as follows.
Sales Returns Book:
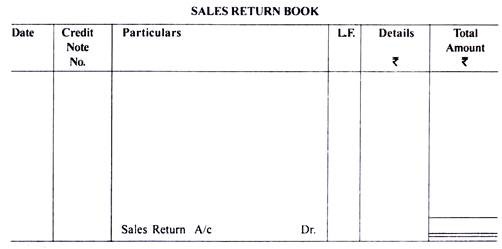
Sales return book is the contrary book for sales day book. This book records the transactions of sales returns made during a day against the respective sales. These sales returns are finally reduced from the value of sales and also adjusted from the balance due from the buyer or the customer. This book is also called as Returns inwards book. The returns made by the customers are acknowledged by raising a Credit note for that amount of returns like invoice in case of a sale. These credit notes have to be serially numbered and should have a reference of the goods and the invoice against which the return is made. The entity debits the sales returns account for reducing the value of sales and credits the customer account to reduce his liability to pay the debt. The common reasons for sales returns are,
- Excess quantity shipped,
- Wrong items or defective items shipped,
- Quality not as per the standard of the customer,
- Specifications of the order don’t match with that of the goods sent etc.
Purchases day book:
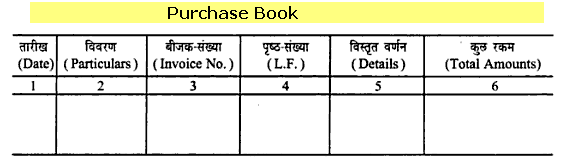
Purchase book which is also called purchases journal is the book maintained by the entity to record all the transactions of credit purchases made by the company. This is the base for verification or reconciliation of stock in the entity. After the internal process of the company ( Raising material requisition order from the manufacturing department and the stores department if the required quantity not available with the company, issues Purchase requisition note containing the details of items to be purchased and the quantity to the purchase department. The Purchase department gets quotations from various suppliers and then selects the best supplier and then obtains the estimation or proforma invoice from that supplier. The purchase department then sends the proforma invoice to the accounts department for release of funds to complete the purchase and then the purchases are made), the purchases are recorded and the total of it is carried to Purchases ledger.
Purchase returns book:
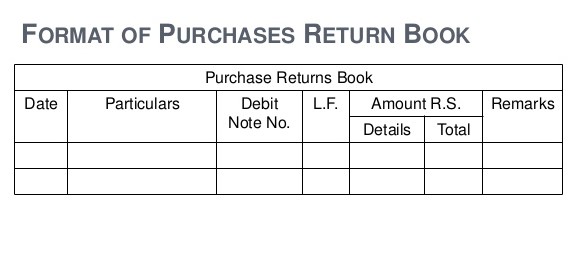
This is also called Returns outwards book. Purchases made by the entity is returned back to the supplier due to various reasons like Quality not as per the requirement, Wrong items sent by the supplier or specifications not as per the order placed etc. When the returns are made, a Debit note is raised by the entity and is sent to the supplier as intimation with respect to the returns made. These debit notes shall be serially numbered and has to be mentioned against each return made by the entity. The returns outward book is totalled at periodical intervals and transferred to purchases book and then netted of against the total purchases in the income statement.
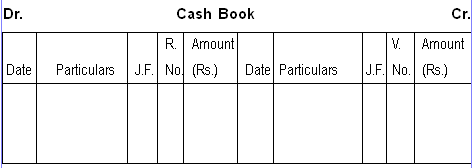
Cash Book:
Cash book is maintained by the entity recording all the transactions made in cash like cash sales, cash purchases, cash used for daily running of expenses or operating expenses, accounts payable paid in cash, accounts receivable received in cash, withdrawals and deposits from bank etc. This cash book is periodically reconciled with the bank statements. Cash book is a substitute for Cash account.
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.