Accounting Concepts, Principles And Conventions

Accounting Concepts
Basic concepts of accounting governs the various aspects and procedures of accounting and helps to maintain and prepare accounting records and financial statements in a better, understandable, comparative and a uniform manner. The concepts of accounting are as follows:
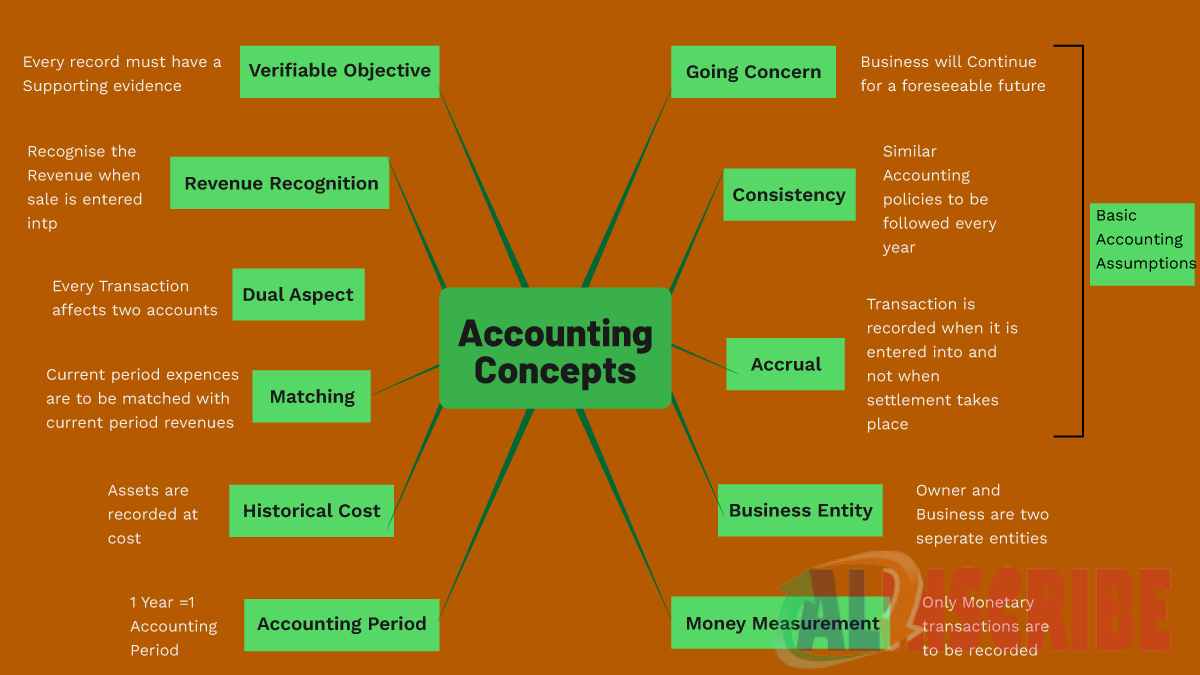
ACCRUAL CONCEPT
This concept basically deals or mentions when to record a transaction. Under accrual concept while book keeping, transactions are recorded at the time of happening and not at the time of payment or receipt of cash and bank. It enforces the books to be prepared as and when they are occurred and not on a subsequent date. It is one of the fundamental accounting concepts.
CONSISTENCY
The objective of consistency concept is to ensure and facilitate the users of financial statements in comparison of financial statements of multiple periods to be made easily and reliable. Consistency is one among the three fundamental accounting concepts. Once if an accounting policy is selected and applied, the accountant should follow the policy consistently and on a going concern basis.
GOING CONCERN CONCEPT
Going concern is the third fundamental accounting assumption which ensures the existence and ability to carry on business for foreseeable future period. It assumes that the business will be running and remains in operation in the foreseeable future period. Deferring of expense and income is based mainly on going concern concept.
MONEY MEASUREMENT CONCEPT
For recording a transaction, it is necessary to measure the transaction in terms of money. Generally money means the local currency of market.
MATCHING CONCEPT
Under this concept, expenses arising due to or in course of earning revenue should be recorded in the same period. Such expenses or income should not be deferred to ensure matching concept .To ascertain the correct profit of the given period all the related expenses and revenues should be recorded in the same accounting period i.e all the expenses relating to the revenue generated in an year is to be accounted. This is because if a transaction is recorded under double entry book keeping, the dual effect of transaction always results in matching concept.
ACCOUNTING YEAR CONCEPT
Business depending upon its operations, generally fixes the accounting year or the financial accounting year as a period of 12 months, which is a year. In such a period the accounting cycles are to be completed. Some business chooses quarterly, monthly, half yearly or annually depending upon their need as its accounting period. It can be as per calendar or fiscal year. Generally accounting period of 12 months is between April - March.
DUAL ASPECT CONCEPT
Double entry book keeping, which corresponds debit for every credit made in the books of accounts, ensures the completeness of transaction. Until both the aspects i.e credit and debit of a transaction is entered, the recording process of the transaction will not be completed.
REALISATION CONCEPT
To realise an income or profit, it should arise and be earned first. This concept ensures that the profit in connection with a transaction should be only taken into the books of accounts when it is earned.
CONSERVATISM CONCEPT
Conservatism concept ensures that anticipated (expected) profit is not recorded. But anticipated loss should be recorded. Revenues or incomes should be only recognised when there is reasonable certainty of its realizing. Expenses can be recorded at the moment when there arises a reasonable possibility of expenses in future.
MATERIALITY CONCEPT
For the purpose of accounting, only material transaction which has some financial effects on the business should never be ignored. A business should record the transaction when not doing so might influence, change or may even communicate an different Information to the users of Financial statements.
Accounting Conventions
Accounting Conventions helps out in accounting when specific guidelines are present.
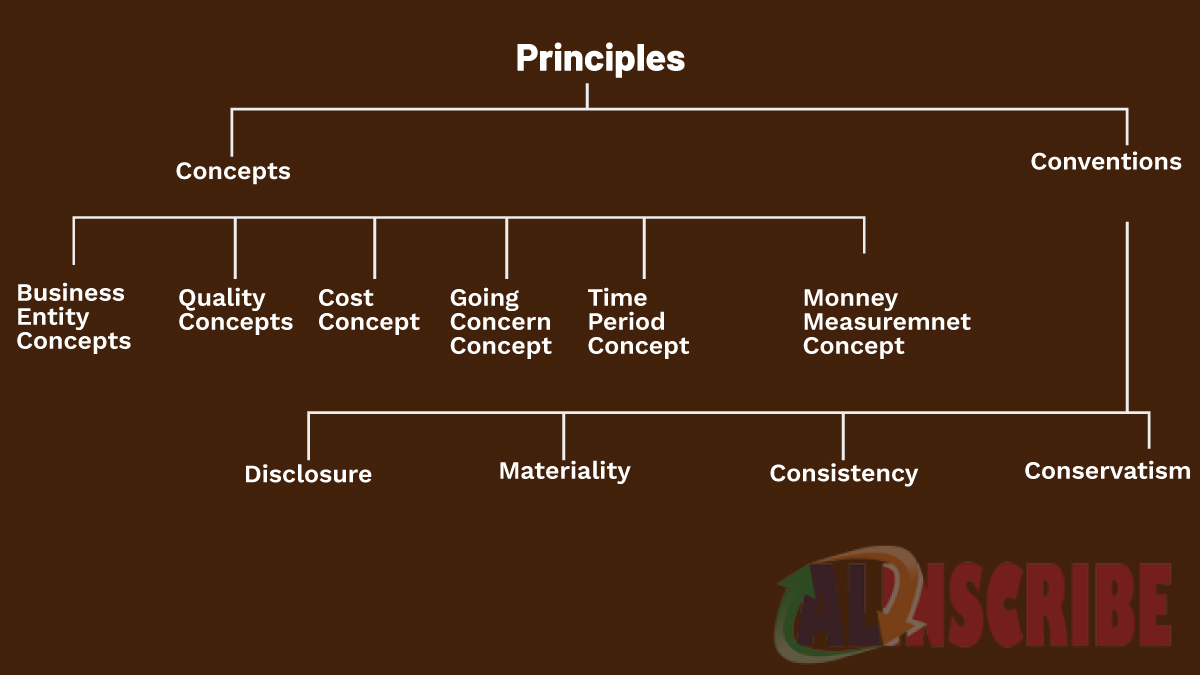
It is a common practise which gives guidelines in those situations where accounting standard fails to govern a specific situation. The four main accounting conventions followed in day to day accounting practises are as follows:
FULL DISCLOSURE
All the information should be fully disclosed to the users. All the facts should be revealed which is material can be both favourable and unfavourable to the business.
Other Conventions of accounting are
- Conservatism
- Consistency
- Materiality
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING

These are the general and essential guidelines or the decision making rules that govern the overall accounting process and helps the development of accounting techniques. It helps in figuring out how to record and maintain transactions and records. The principles of accounting are:
REVENUE RECOGNITON
It mainly deals with recognising the income and revenue of the business in various accounting stages and financial statements. The gross inflow of cash or cash equivalents to the business is called revenue. These inflows can be receivables or any other considerations arising in the course of ordinary business activities of the enterprise. Revenue includes dividends, interests, royalties, etc. and excludes the amount that is collected on behalf of another person or a third party.
HISTORICAL COST CONCEPT
An asset when purchased is normally recorded in the books of accounts at the respective invoice price. The amount thus paid for the acquisition becomes the cost basis for further transaction and adjustments during both the period of acquisition and subsequent accounting periods. To value an asset, historical cost is the most easily available, reliable and verifiable source.
MATCHING PRINCIPLE
Accrual concept of accounting is the base for matching principle. As per matching principle, expenses incurred in earning some revenue should be treated in the same accounting period for the purpose ascertaining the correct profit. In this concept, actual timing and actual cash inflow and outflow are ignored or disregarded. Occurrence is the place where revenue and expenses are given importance. Example for the matching concept can be said as, if the revenue from sales of some goods is recognized; cost of such goods sold should be also taken at that period itself.
FULL DISCLOSURE PRINCIPLE
All the information should be fully disclosed to the users. All the facts should be revealed which is material that could be both favourable and unfavourable to the business. Financial statements should be conveying and not concealing. For the relevant and reliable information, it is necessary that the accounted information should be full with its substance and economic reality and not merely with its legal form.
OBJECTIVITY
The ultimate requirement of the principles is that the accounting information or data should be free from errors or bias. Financial statement should be based on solid evidence, this means accounting entries are fact based and not affected by personal opinions and feelings and the main object of preparing financial statements is to convey the results and details of the transactions of the business to the users of financial information.
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.