ERP And Business Intelligence: Why Your Business Needs Both

Data is the king in current market scenario. Implementation and incorporation of right data is crucial for staying competitive in this era. This is exactly why businesses need some specific tools to help them in achieving the same without having to face many complexities.
ERP and Business Intelligence (BI) are two of the most important tools to collect, leverage and put business related data in work. However, businesses often tend to think only one of these tools are enough, which is certainly a misconception. You need both of the tools to give your business a new height.
In this article we will discuss what ERP systems and Business Intelligence are and why do your business need both of the tools. There will be some basic information regarding both of the tools, which will closely be followed by detailed information on the topic.
You can also read Why Business Intelligence (BI) Needs To Be Integrated With ERP Systems for learning about how BI and ERP integration works to benefit your business.
What is Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence (BI) can be considered as a combined formation of business analytics, data tools, data visualization, data mining and data infrastructure. BI also promotes the best practices that can help an organization to grow while making more data-driven decisions.
Modern Business Intelligence allows you to gain a comprehensive view of all the data associated with your organization. You can use that data to drive organizational changes, eliminate errors, and implement effective strategies. With the help of this, you can also adapt to market changes faster than ever.
Emergence of Business Intelligence
Traditional business intelligence was first introduced in the year of 1960. Back then it was a system used for sharing information across various organizations. The term ‘Business Intelligence’ was first coined in 1989. This time the system emerged alongside computer models, which were to be used for decision making.
Modern BI emerged from those computer programs, getting more and more advanced until it took today’s shape.

How does Business Intelligence work?
Each business organization has a goal that keep them afloat and drive them towards ultimate success. In order to achieve the goal, it is crucial for them to collect data and put that in work to extract as many benefits as possible. Analyzing data is also a critical part of making important decisions with effectiveness and efficiency.
However, collecting, storing and analyzing data is not at all an easy task to complete. At first data is processed, which is then stored in data warehouses, in applications, in cloud and so on. Performing all of it manually is as troublesome as it is prone to mistakes. Thus, businesses need a technical tool that can perform all of it automatically while enhancing productivity and speed of the entire process.
BI platforms usually offer data visualization tool as well. These tools are capable of converting data into graphs and charts, which makes it easy to understand and visibly pleasing to be presented in front of the shareholders and decision makers.
Different methods used by BI
Business intelligence is a layered phenomenon. The term covers several methods that make BI work. Methods of collecting, storing and analyzing data from different business operations as well as activities in order to implement performance optimization.
Some of the most common and integrated methods used by BI are listed below,
Data mining
Data mining is performed by using databases, machine learning, and statistics. It helps in uncovering trends in large datasets.
Performance metrics and benchmarking
Performance metrics are determined by comparing current performance with historical performance data in order to track performance that went against goals along with possible reasons behind the same while using customized dashboards.
Advanced reporting
Advanced reporting features that boast interactive charts and graphs, making it easy to be shared with key stakeholders to make decision easily.
Querying
BI makes query easy. Thus, when you ask a data-related question, BI pulls out the answer from data sets.
Descriptive analytics
BI uses preliminary data analysis for finding out analytical answers.
Statistical analysis
BI takes out the results from descriptive analysis and uses the results for exploring data using statistics for finding answers to several why and how questions.
Visual analysis
Through visual analysis BI explores data via several tools such as visual storytelling, which enables better access to insights while keeping the flow of analysis.
Data visualization
This is the method of turning data into visual representation, such as graphs, histograms and charts.
Data preparation
This method includes compilation of data sources, identification of measurements and dimensions and preparation of data analysis.
Business Intelligence statistics
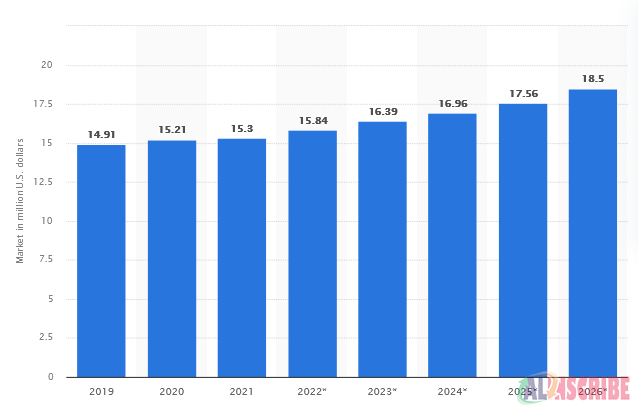
The above picture depicts the market size of Business Intelligence and analytics software. By the end of 2023, the market is forecasted to cross $16.39 million mark. And by 2026, the numbers are expected to soar and reach $18.5 million, providing a better opportunity for BI and ERP integration to offer businesses a new peak of success.
What is an ERP system?
ERP, Enterprise Resource Planning, systems are a software solution that help a company in managing their resources. These resources can include employees, finances, materials and so on.
Some of the primary components of ERP solutions are Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Human Resource Management (HRM), Financial Accounting & Reporting (FAR), Supply Chain management (SCM), and Project Management. Apart from these primary components, ERP systems can also be used for warehouse management, inventory management, asset tracking etc. However, very few ERP solutions sport all of these features together in one interface. Tactic ERP & CRM is one of those very few solutions.
An ERP system includes multiple modules, each of the module is capable of taking care of several daily activity of a business. Sales, marketing, manufacturing, purchasing, day-to-day expenses are some of these activities that can easily be managed with the help of an ERP system.
Emergence of ERP systems
Traditional systems, which can be considered as the very first form of ERPs, were used only by the large organizations. Organizations with bigger budgets and bigger operations were the only one to be able to afford these systems.
However, when small and medium-sized businesses started emerging, the industry started requiring a much comprehensive and easier system to be used for managing the business without having to invest a hefty amount.
ERP systems first emerged from Material Requirements Planning (MRP) software and from there it started evolving and took the shape of what it is today. These days, ERP systems are more dynamic and capable of adapting to the needs of an organization regardless of the size.
Types of ERP systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are software solutions that help organizations manage and integrate various aspects of their business processes, such as finance, human resources, procurement, supply chain, manufacturing, and more. Hence, it is very natural for the software to be offered in different categories. There are a number of types associated with ERP systems, which can be categorized based on different criteria. Here are some common ways to categorize ERP systems:
Based on Deployment
- On-Premises ERP: These systems are installed and run on the organization's own hardware and servers. The organization is responsible for maintenance, upgrades, and security.
- Cloud ERP: Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet. They offer scalability, flexibility, and reduced IT infrastructure costs.
Based on Size and Complexity
- Small and Medium-sized Business (SMB) ERP: Designed for smaller organizations with simpler requirements. These systems are typically more cost-effective and easier to implement.
- Enterprise ERP: Tailored for large, complex organizations with extensive needs. They often support multiple locations, business units, and international operations.
Based on Industry Vertical
- Industry-Specific ERP: These systems are customized or specialized for specific industries like manufacturing, healthcare, retail, or education. They often include industry-specific features and best practices.
Based on Functionality
- Core ERP: These systems cover essential functions like finance, HR, and supply chain management.
- Extended ERP: These systems go beyond core functions and may include customer relationship management (CRM), business intelligence, e-commerce, and other specialized modules.
- Open Source ERP: ERP systems that are built on open-source technologies and can be customized and extended by the user or developer community.
ERP Suites vs. Best-of-Breed
- ERP Suites: Comprehensive systems that cover a wide range of business functions within a single software package. All modules are integrated, which can simplify data sharing and reporting.
- Best-of-Breed: Organizations choose specialized software for different business functions (e.g., separate HR, CRM, and financial systems) and integrate them to meet their specific needs.
- Mobile ERP: These systems are designed to be accessible and usable on mobile devices, enabling users to access and input data while on the go.
Legacy ERP vs. Modern ERP
Legacy ERP systems refer to older, often outdated systems, while modern ERP systems leverage the latest technologies, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and real-time data analysis.
Custom ERP
Some organizations opt to build their ERP systems from scratch or heavily customize existing ERP solutions to precisely meet their unique requirements.
Two-Tier ERP
Large organizations may implement a two-tier ERP strategy where they have one primary ERP system for core functions and a separate, often simpler, ERP system for subsidiary or regional operations.
The choice of ERP system depends on an organization's size, industry, specific business needs, budget, and technological preferences. Selecting the right type of ERP system and its features is crucial to improving business efficiency, data accuracy, and decision-making capabilities.
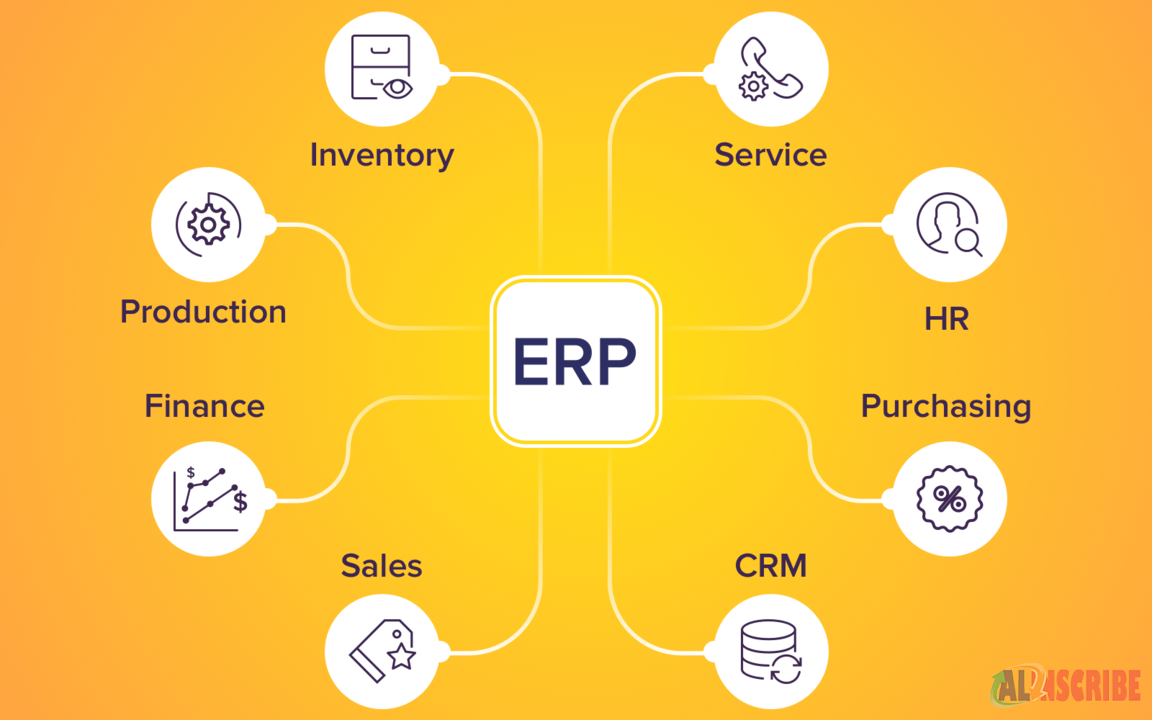
Why should BI be integrated in ERP systems
Business Intelligence (BI) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems serve distinct but complementary purposes within an organization. Integrating BI and ERP systems can offer several advantages:
Enhanced Decision-Making
BI tools provide advanced data analysis and reporting capabilities, allowing users to extract actionable insights from the data stored in the ERP system. This can help decision-makers make informed and data-driven choices.
Real-time Data Access
Integrating BI and ERP systems can provide real-time access to critical business data. This enables users to monitor and react to changes in the business environment promptly.
Data Centralization
ERP systems store a vast amount of data about various aspects of an organization, including finance, inventory, human resources, and more. Integrating BI and ERP systems allows organizations to centralize data, making it easier to access and analyze.
Customized Reporting
BI tools enable users to create customized reports and dashboards tailored to their specific needs. This flexibility can be invaluable for different departments within an organization, such as sales, finance, or production.
Predictive Analytics
BI tools can incorporate predictive analytics, which can help organizations forecast future trends, identify potential issues, and optimize processes. This is especially useful for demand forecasting, inventory management, and financial planning.
Improved Data Quality
Integrating BI and ERP systems can help improve data quality by providing tools to cleanse, validate, and standardize data. This ensures that the data used for analysis is accurate and reliable.
Cross-Functional Insights
ERP systems typically focus on specific business functions (e.g., finance, supply chain, or human resources). By integrating BI, organizations can gain cross-functional insights, uncovering connections and dependencies between different areas of the business.
Self-Service Analytics
BI tools often offer self-service capabilities, allowing non-technical users to create their own reports and conduct ad-hoc analyses. This reduces the burden on IT departments and empowers business users.
Scalability
As an organization grows, its data and reporting needs may evolve. Integrating BI into ERP systems can provide a scalable solution to accommodate increasing data volumes and more complex analytical requirements.
Competitive Advantage
Leveraging BI and ERP systems can give organizations a competitive edge by enabling them to make faster and more informed decisions, optimize processes, and adapt to changing market conditions.
While there are clear advantages to integrating BI and ERP systems, it's essential to plan the integration carefully, ensure data security and privacy, and provide appropriate training and support to users. Additionally, the specific benefits may vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and unique requirements.
Analysis
From the above points it is clear that BI and ERP have their very own way of improving your business. However, those work the best when two of the systems are integrated with each other. There are so many benefits that you can acquire by implementing both of the systems in the course of your business. Thus, opting for an ERP system, which is powered by Business Intelligence can certainly be a wise move for your business.
You can also read Why Business Intelligence (BI) Needs To Be Integrated With ERP Systems for learning about how BI and ERP integration works to benefit your business.
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.