Credit Rating

Credit Rating:
Credit rating is the evaluation of the credit worthiness of an individual or of a business concern or of an instrument of a business based on the relevant factors indicating ability and willingness to pay obligations and also net worth. It establishes a link between risk and return. It provides the confidence to the stakeholders with respect to the company or the instrument.
An investor or any other interested person uses the rating to assess the risk level and compares his expected return with the offered rate of return. Credit rating is a symbolic indication of current opinion regarding the relative capability of a corporate entity to service its debt obligations in time with reference to the instrument being rated. To facilitate simple and easy understanding, credit rating is expressed in alphabetical or alphanumerical symbols.
Credit Rating Agency:
CRA is a body corporate engaged in or proposes to be engaged in the business of rating of securities offered by way of public or rights issue.
Types of credit rating:
Determination of credit ratings mostly depend on the credit agency as they are free to use terminologies as per their preferences. However, most of the time credit ratings are categorized into two different categories, which are investment grade and speculative grade.
- Investment grade: This type of investment is based upon the consideration of credit agency. The issuer is the one to decide the terms of repayment. These types of investment is also more likely to be less competitively priced.
- Speculative grade: this type of investment is the one to possess high risks. Hence, these are also the ones to require higher rates.

Uses of Credit Agency:
Investors use credit rating to compare the relativity ranking of the default loss probability for a given investment with other rated instruments. In the absence of professional credit rating, the investor has to largely depend upon general information of the company and its promoters. This is a risky analysis made by the investors, as not every investor has the knowledge about the instruments and its working. Well researched and properly analyzed opinions in the forms of credit rating helps investors in taking well informed decisions for investments and thus helps in minimizing the risks.
Credit rating enables the market to place immense faith in the Issuers based on the opinion of credit rating and enables the issuers to issue highly rated instruments to access the market even during adverse market conditions.
Credit rating helps the intermediaries such as Merchant bankers for planning, pricing, underwriting and placement of the issues. Intermediaries like brokers and dealers in securities use rating as an input for monitoring risk exposures.
SEBI made Credit rating mandatory for issuers to ensure the protection of the investors in the securities market.
The activities of CRS’s in the Indian Capital market are regulated by SEBI (Credit Rating Agencies) Regulations, 1999.
Credit rating should not be mistaken as Grading. Credit rating is done for debt instruments whereas; Grading is done for Equity shares and Convertible instruments. Credit rating is done and is reviewed on a continuous basis till the securities are redeemed, but Grading is a one-time activity which is performed only at the time of IPO (Initial Public Offer). CRA is mandatory as per the rules of SEBI but Grading is optional i.e it can be performed at the discretion of the company.
The main CRA’s in India are,

- Investment information and Credit rating Agency of India (ICRA),
- Credit rating and information services (India) limited (CRISIL),
- Credit analysis and Research limited (CARE),
- Standard and poor’s corporation,
- FITCH credit rating India private limited.
Registration of a Credit Rating Agency:
According to the SEBI (Credit Rating Agencies) Regulations, 1999,
Any person proposing to commence any activity as a credit rating agency shall make an application to the board for the grant of a certificate of registration in Form –A. The Board, on being satisfied that the applicant is eligible, shall send intimation to the applicant mentioning the category for which the applicant has been found eligible for the grant of the certificate of registration. The certificate of registration is granted in Form –B.
This certificate of registration shall be held valid for life time unless it is suspended or cancelled by the Board.
Eligibility to act as Promoter of Credit Rating Agency:
SEBI will only consider an application unless it is promoted by a person belonging to any of the following categories,
- A public financial institution,
- A scheduled commercial bank,
- A foreign bank operating in India with the approval of the RBI,
- A foreign credit rating agency recognized under Indian Law and having at least five years experience in rating securities,
- Any company or body corporate, having continuous net worth of minimum Rs. 100 crore as per its audited annual accounts for the previous five years in relation to the date on which application has been made to SEBI seeking registration.
Eligibility criteria to become a CRA:
The applicant if satisfies the following conditions is eligible to act as a CRA;
- The applicant is set up and registered as a company under the companies act,
- The applicant in its MOA (Memorandum of Association) has specified rating activity as one of its main objects,
- The applicant has a minimum net worth of Rs.5 crores,
- The applicant has adequate infrastructure to enable it to provide rating services,
- The applicant and the promoters of the applicant have professional competence, financial soundness and general reputation of fairness and integrity in business transactions to the satisfaction of SEBI,
- Neither the applicant nor the director, promoter has been involved in any legal proceeding connected with the securities market, which may have an adverse impact on the interests of the investors,
- Neither the applicant nor its promoters, directors, has at anytime in the past been convicted of any offense involving moral turpitude or any economic offense,
- The applicant has, in its employment, persons having adequate professional and other relevant experience to the satisfaction of the SEBI,
- The applicant in all other respects is a fit and proper person for the grant of a certificate.
Code of Conduct:
Every CRA is required to abide by the Code of Conduct as per SEBI Regulations:
- A CRA shall make all efforts to protect the interests of the investors,
- A CRA, in the conduct of its business shall observe high standards of integrity, dignity and fairness in the conduct of its business.
- A CRA shall fulfill its obligations in a prompt, ethical and professional manner.
- A CRA shall at all times exercise due diligence, ensure proper care and exercise independent professional judgment in order to achieve and maintain objectivity and independence in the rating process.
- A CRA shall have a reasonable and adequate basis for performing rating evaluations, with the support of appropriate and in depth rating researches. It shall also maintain records to support its decisions.
- A CRA shall have in place a rating process that reflects consistent and international rating standards.
- A CRA shall not indulge in any unfair competition nor shall it wean away the clients of any other rating agency on assurance of higher rating.
- A CRA shall keep track of all important changes relating to the client companies and shall develop efficient and responsive systems to yield timely and accurate ratings. Further a CRA shall also monitor closely all relevant factors that might affect the creditworthiness of the issuers.
- A CRA shall disclose its rating methodology to clients, users and the public.
- A CRA shall, whenever necessary, disclose to the clients, possible sources of conflict of duties and interests, which could impair its ability to make fair objective and unbiased ratings. It shall also ensure that no conflict of interest exists between any member of its rating committee participating in the rating analysis and that of its client.
Monitoring of Ratings:
CRAs should during the lifetime of securities which were rated by it, continuously monitor the rating of such securities. It should also disseminate information regarding newly assigned ratings and changes in earlier rating promptly through press releases and websites and in the case of securities issued by listed companies, such information should also be provided simultaneously to the concerned stock exchanges where those securities are listed.
It is the obligation to appoint a Compliance officer who will be responsible for monitoring the compliance of the act, rules and regulations, notifications, guidelines, instructions etc issued by SEBI or the Central government. The compliance officer should immediately and independently report to SEBI any non-compliance noted by him.
Every CRA shall maintain its books of accounts, records and other useful documents for a minimum period of 5 years.
Every CRA has to conduct Internal audited on a half-yearly basis as per the Regulation 22 of the SEBI (Credit Rating Agencies) Regulations, 1999 by Company secretaries (CS), Chartered Accountants (CA) or Cost and Management Accountants (CMA), who are in practice and who do not have any conflict of interest with the CRA and the audit so done shall cover all aspects of CRA operations and procedures, including investor grievance redressal mechanism, compliance with the requirements stipulated in t SEBI act, Rules and Regulations made thereunder and guidelines issued by SEBI from time to time.
Rating symbols of various CRAs:
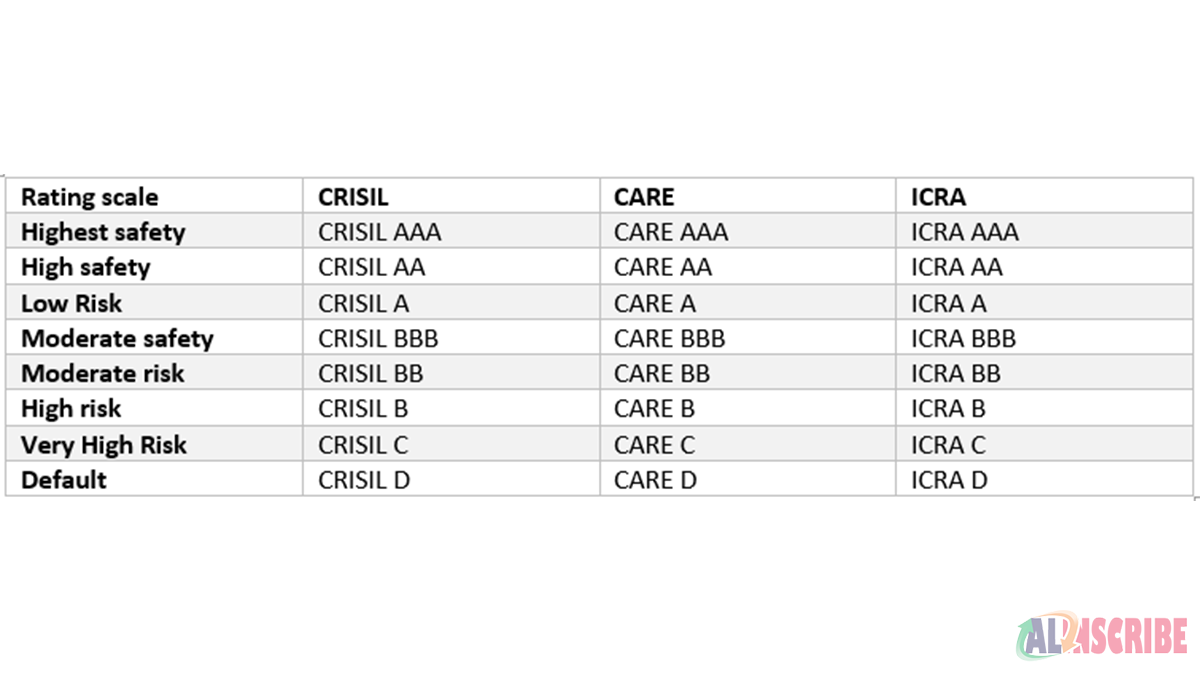
CRISIL:
The rating mechanism of CRISIL starts with AAA or Triple A being the highest rank that is highest safety to invest and there has been timely payment of interest and principal, followed by

AA or Double A – A minor variation from AAA where AA also bears high security with timely payment of Interest and principal,
BBB or Triple B – Moderate Safety regarding the timely payment of Interest and principal subject to variations caused by changing circumstances,
BB or Double B – Inadequate safety regarding timely payment of Interest and principal,
B - High risk,
C - Substantial risk
D - Default rank or Default risk.
ICRA:

The ranking in ICRA starts from LAAA being highest safety rank followed by LAA, LA, LBBB, LBB, LB and LC, being the Substantial Risk bearing securities’ rank and LD being Default risk.
CARE:

The ranking for CARE starts from CARE AAA being highest safety rank followed by CARE AA, CARE A, CARE BBB, CARE BB, CARE B, CARE C and CARE D holding the lowest category.
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.