Mutual Funds - Introduction
Mutual fund is a trust that pools the savings (accepts the money) of a number of investors who share a common financial goal that is to earn return or create wealth). Mutual Fund offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified professionally managed basket of securities at a relatively low cost. It is a invest scheme that is run by Asset management company (AMC) who are professionally qualified in investing the funds of investors.
When the investors give money to the mutual fund, they will be allotted Units of the mutual fund scheme. Asset management company invests the funds pooled from the investors and invests them in different schemes. Units are the share of holdings in a scheme that a investor holds.
Parties involved in Mutual fund establishment:
- Sponsor
- Trustee
- Asset management company
- Custodian
- Fund managers
Sponsor:
A sponsor means a corporate who, acting alone or in combination with another body corporate establishes a mutual fund according to the SEBI regulations.
The Sponsor of a mutual fund is like a promoter of a company providing capital for starting of company. The sponsor should be a body corporate in the business of financial services for a period not less than 5 years and should be financially sound in the view of SEBI.
A sponsor should contribute a minimum value as a percentage of Net worth of the AMC, which is presently 40%.
Trustee:
A mutual fund is to be formed as a Trust under the Indian Trust act. The trust should have a deed registered under the provisions of Indian Registration Act, 1908. This trust deed acts as the basis for the terms of agreement and shall contain the clauses specified in the Third schedule of the regulations. A trustee shall hold the property of the Mutual fund in good faith or in trust for the benefit for the Unit holders.

Asset Management Company:
An Asset Management Company commonly referred as AMC is a corporate appointed to look after the affairs of the mutual fund trust and its schemes. It should be a corporate approved by SEBI and it should be formed as a “Limited Liability Company” with a minimum net worth of Rs. 10 crores.
Custodian:
A custodian is a financial institution that maintains and safeguards the assets of the Mutual funds. It acts as a Transfer agent and regulates the transactions of the Mutual funds like purchases and sales, movements in the unit holder’s funds.
A mutual fund custodian is appointed by Mutual Fund Company only if the custodian possesses a valid registration certificate issued by SEBI authorizing it to have the custody of the securities and assets of the Mutual fund. In case of dematerialized securities, the custodian is replaced by the Depository Participant.
Fund Managers:
Fund managers are the individuals or a group of individuals under the AMC managing the funds of the investors deciding on matters like where to invest and which one gives good return.
Types of Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds are classified into
- Open ended funds
- Close ended funds
- Money market funds
- Fixed income funds
- Equity funds
- Balanced funds
- Index funds
- Exchange Traded Funds (ETF),
- Specialty funds
- Fund of Funds
Types of mutual funds are explained below:
NAV:
“Net Asset value” or NAV is the value or the share of the company’s worth a person would receive if the company is wound up. The valuation depends on the valuation of nature of assets. This NAV is calculated by the AMC on every business day. NAV also refers to the value at which investors may apply to a mutual fund for joining a scheme. The investment of the investor is treated as Capital of the AMC and the investment made by the AMC is treated as an asset. A Mutual fund may have different schemes and NAV is calculated separately for each and every scheme. The value of portfolio is the aggregate value of different investments. Since Mutual fund investments are marked to market, the value of Investments for computing NAV will be at market value. According to Regulation 48 of SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations, mutual funds are required to compute Net Asset Value (NAV) of each scheme and to disclose them on a regular basis – daily or weekly (based on the type of scheme) and publish them in atleast two daily newspapers.

Returns:
Returns are derived by investors in following forms
- Cash dividend – Dividend issued by the Mutual fund Company in the form of cash to the unit holders.
- Capital gain – Capital gain to the unit holders arise when the market value of the Units are increased.
- Change in Fund’s NAV – When the fund’s NAV is increased, the Unit holders get a share in it and their value is increased.
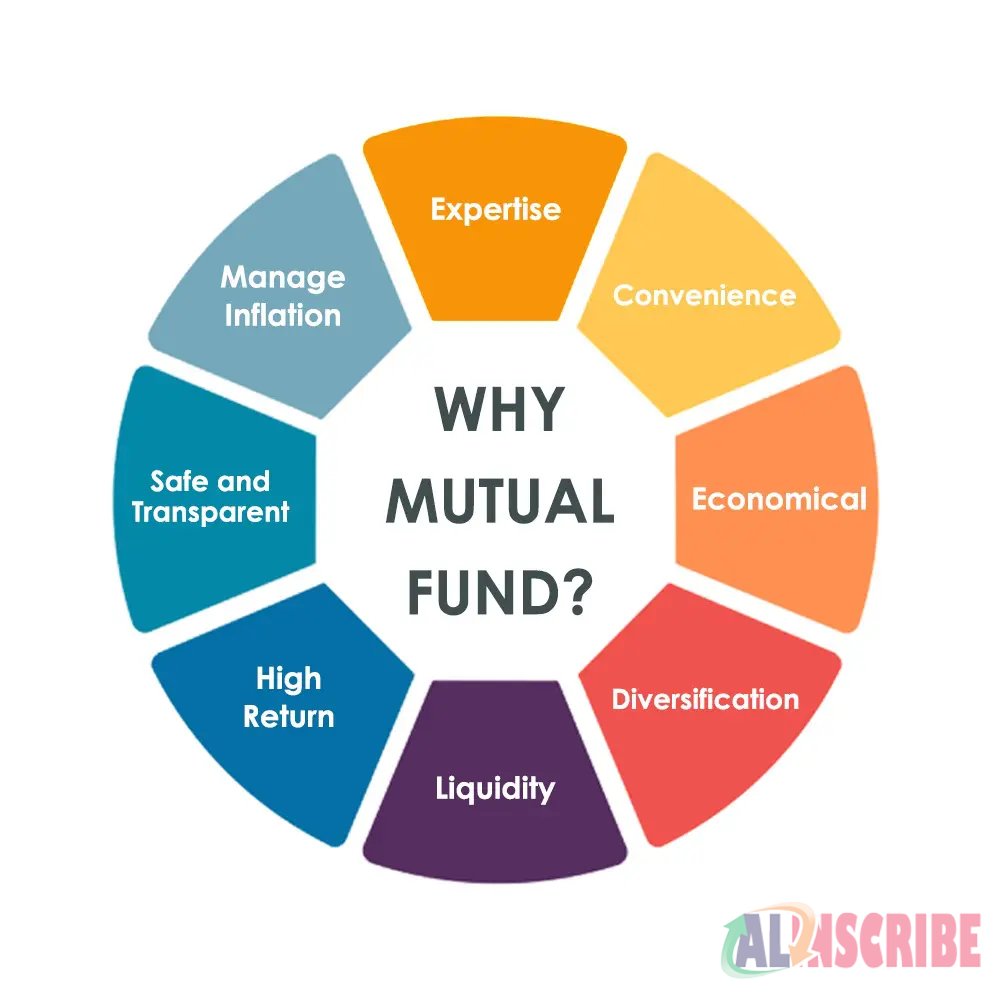
Since the funds are managed by professional managers or fund managers who are backed by dedicated investment research team which analyses the performance and prospects of the companies to invest and the funds are diversified into various industries and sectors. Mutual funds are relatively less expensive and to invest and earn huge returns. All the Mutual funds are regulated by SEBI (Securities Exchange Board of India) as per the Mutual Funds regulations. The main advantage is that an investor can opt for SIP (Systematic Investment Plan), Systematic Withdrawal plan etc, providing the investor to invest and withdraw as per the requirements. Mutual funds involves some fees like Entry load, Exit load, fee paid to asset management company etc.
Related Read: Types of Mutual Fund
Article Comments
Similar Articles
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.