Flame Retardants

Flame retardants are a key component in decreasing the devastating impact of fires on people, property, and the atmosphere. They are added to or treat flammable substances, including textiles and plastics. The word “flame retardant” refers to operate, not a family of chemical substances. A variety of chemicals, with different qualities and constructions, act as flame retardants and these chemicals are generally combined for effectiveness.
The normal elements in flame retardants
Bromine, phosphorus, nitrogen, and chlorine are traditionally utilized in flame retardants. Inorganic compounds are also used in flame retardants, either individually or as a part of a flame retardant system in conjunction with bromine, phosphorus or nitrogen. It is most important to note that flame retardants are not without always interchangeable. Their areas of software are regularly unique and substitution may also be complex.

The Working mechanism of fire retardants
Flame retardants are added to specific substances or applied as a therapy to substances (e.G., textiles, plastics) to avert fires from starting, limit the spread of fireside and slash fire damage. Some flame retardants work effortlessly on their own and others act as “synergists” to increase the fireplace protecting advantages of alternative flame retardants. The flames retardants are essential due to the fact substances that have to be made fire-resistant are very different from their bodily nature and chemical composition, in order that they behave in another way during the course of combustion. The elements in flame retardants additionally react otherwise with fireplace. As a result, flame retardants have to be matched safely to each variety of fabric. Flame retardants work to discontinue or delay fire, however, depending on their chemical makeup, they have interaction at one-of-a-kind phases of the heart cycle. To better understand how flame retardants work, it’s important to fully grasp the fire cycle:
- Preliminary ignition source may also be any heat supply (e.G., warmth, incandescent fabric, a small flame).
- Ignition supply makes the fabric to burn and decompose (pyrolysis), releasing flammable gasses.
- If stable substances do not damage down into gasses, they continue to be in a condensed section. Throughout this segment, they're going to slowly smolder and, on the whole, self-extinguish, especially in this event they “char,” which basically means the fabric creates a carbonated barrier between the flame and the underlying fabric.

- Within the gas section, flammable gasses are released from the fabric and they are blended with oxygen from the air. Within the combustion zone, or the burning section, fuel, oxygen and free radicals combine to create chemical reactions that purpose visible flames to show up. The fire then becomes self-sustaining due to the combustion process and it continues to burn the fabric due to which extra flammable gasses are released, feeding the combustion method.
When flame retardants are present within the fabric, they are able to act in three key ways to discontinue the burning approach. They will work to:
- Disrupt the combustion stage of a heart cycle, together with heading off or delaying “flashover,” or the burst of flames that engulfs a room and makes it way more intricate to flee.
- limit the process of decomposition with the aid of physically insulating the available fuel sources from the fabric supply with a fireplace-resisting “char” layer.
- Dilute the flammable gasses and oxygen concentrations within the flame formation zone through emitting water, nitrogen or different inert gasses.
The variations between fireplace retardants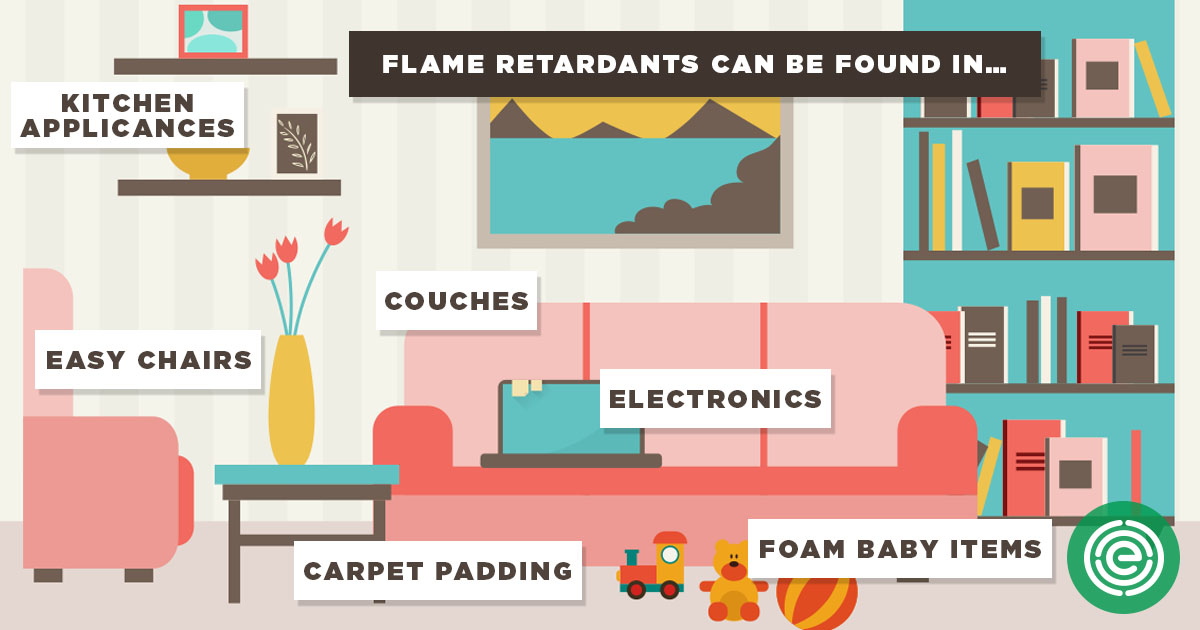
Flame retardants are usually not similar, and they don't seem to be similar either in relation to the fire safety of substances and products. A variety of flame retardants is required considering the factors that different flame retardants react in a different way with fire. Moreover, materials that have to be made fireplace-resistant are very distinctive of their bodily nature and chemical composition, and so they behave in a different way throughout combustion. Therefore, chemical producers have developed extraordinary flame-retardant chemistries to match specific merchandise to make them fireplace-resistant and enable them to maintain their meant functionality and efficiency necessities. Further innovation by the chemical manufacturing industry might be required to keep percent with advancements in technological know-how, and, with it, a constant broaden in new merchandise.
Article Comments
Articles Search
Sponsor
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.
There are zero sub-categories in this parent category.